Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
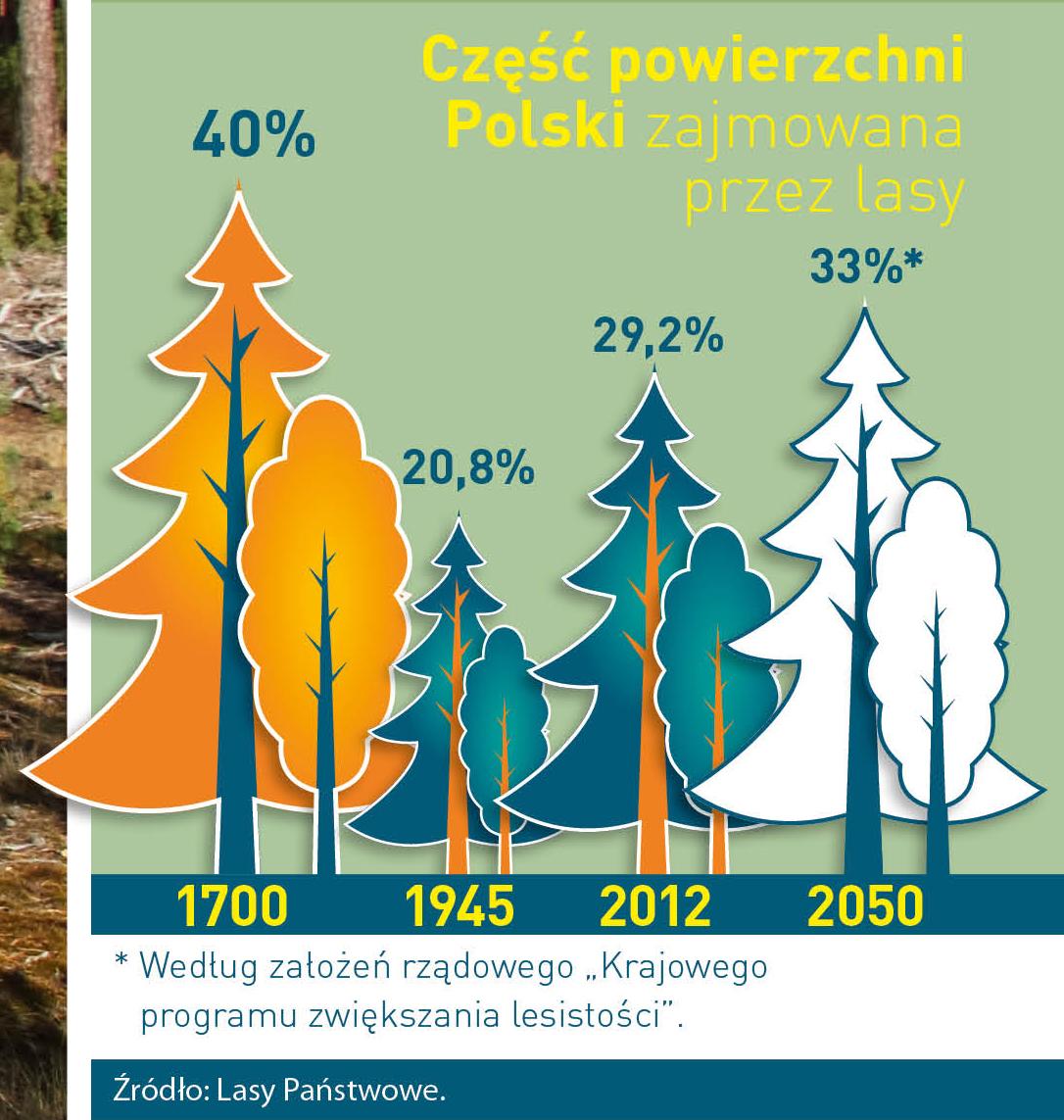
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Uratowany myszołów
Uratowany myszołów
Czasami nasze codzienne zadania przerwie nieoczekiwane zdarzenie. Tym razem leśniczy Leśnictwa Aleksandrowiec, w trakcie wykonywania czynności służbowych, dostrzegł w pobliżu leśnej drogi osłabionego myszołowa, który nie mógł wzbić się do lotu.
Leśniczy na miejsce wezwał patrolującą w pobliżu Straż Leśną. Szybko zapadła decyzja, żeby myszołowa złapać i przetransportować do Ośrodka Rehabilitacji Dzikich Zwierząt Jeleniagóra w sąsiednim Nadleśnictwie Zamrzenica. Na miejscu po wstępnych badaniach nie stwierdzono żadnego urazu, ale znaczne osłabienie i spadek wagi. Myszołów znalazł pomoc i trafił pod fachową opiekę, nam pozostaje teraz trzymać kciuki za jego powrót na łono przyrody.
Przedstawiamy Państwu kilka przydatnych wskazówek, jak zachować się, gdy podczas leśnych wędrówek trafimy na ranne, porzucone, czy też martwe zwierzę.
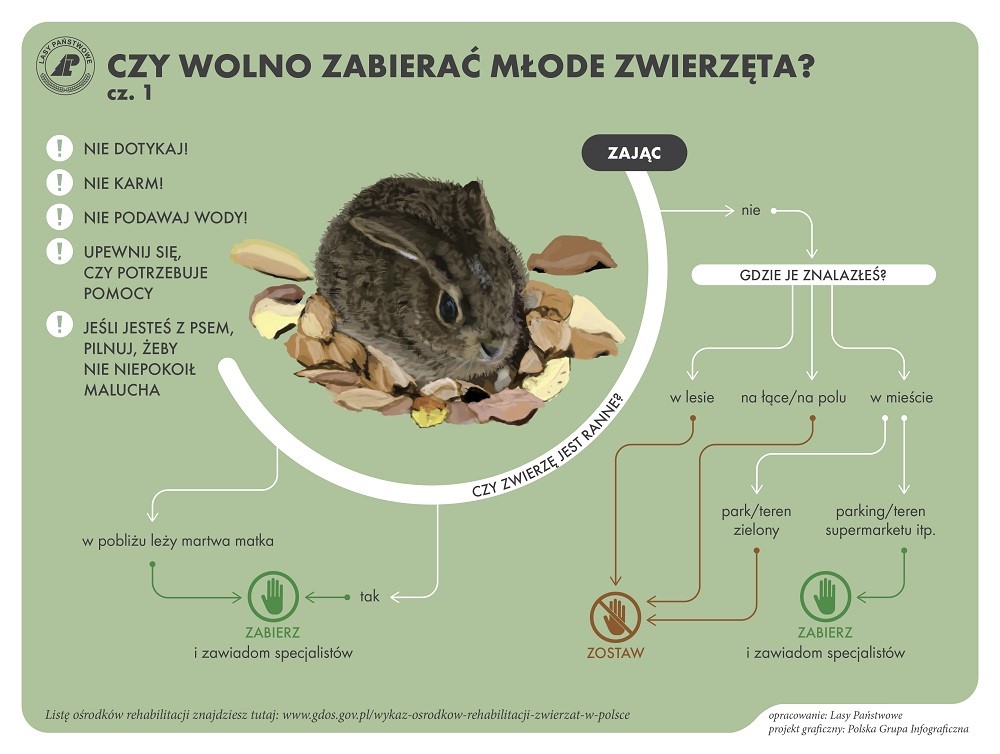
Co robić, gdy spotkamy ranne zwierzę?
Należy zachować szczególną ostrożność, nie zbliżać się bez potrzeby do takich zwierząt. Pomocy można szukać u leśników, choć najlepiej powiadomić o tym urząd gminy. To gmina ma bowiem zgodnie z ustawą o ochronie zwierząt obowiązek opieki nad wszystkimi zwierzętami: domowymi i dzikimi – zapewnienia im ewentualnego schronienia czy opieki weterynaryjnej. W tym zakresie gmina może liczyć na współpracę i pomoc ze strony członków Polskiego Związku Łowieckiego, których zobowiązują do tego przepisy.
Co zrobić, gdy natrafisz w lesie na martwe zwierzę?
Jeśli znajdziesz w lesie padłe zwierzę, niezależnie od tego czy jest to zwierzę domowe czy dzikie, nie przechodź obok niego obojętnie. Śmierć zwierzęcia może być skutkiem choroby zakaźnej. Truchła nie wolno dotykać ani tym bardziej zabierać.
Koniecznie trzeba powiadomić urząd gminy, a następnie nadleśnictwo. Usunięcie i utylizacja martwych zwierząt jest obowiązkiem gminy. Nadleśnictwo należy powiadomić dlatego, bo ubytek zwierzyny w obwodzie powinien zostać uwzględniony w planach łowieckich.
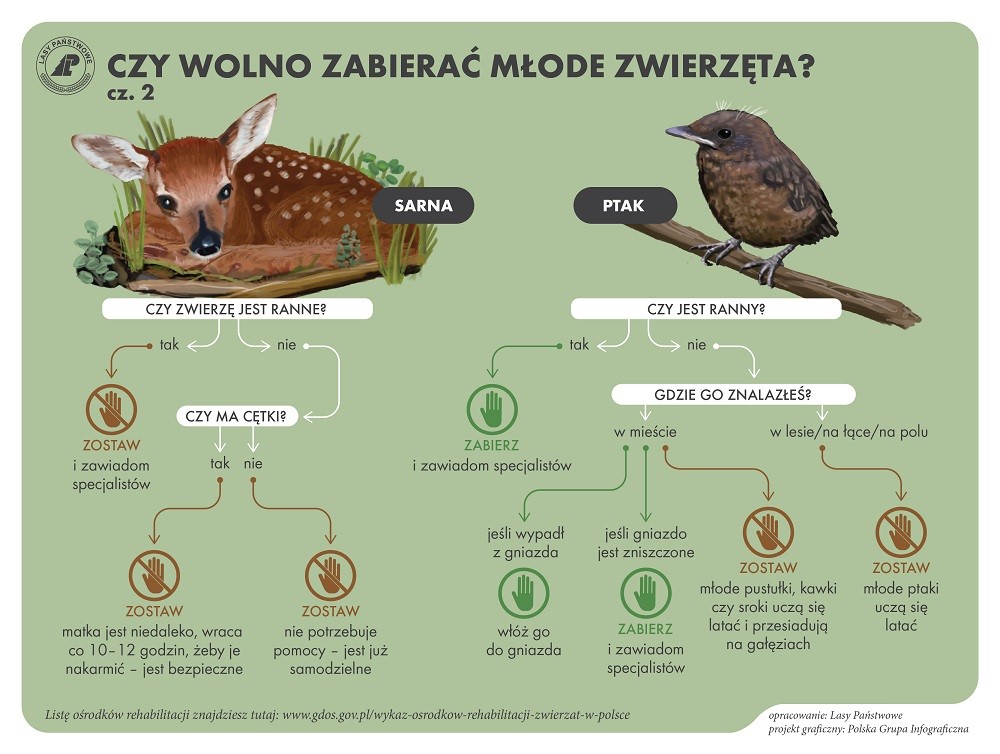
Znajdziesz w lesie młode zwierzę, które podejrzewasz, że zostało porzucone?
Nie wolno zbliżać się do takich zwierząt, dotykać ani też zabierać ich z lasu. W większości przypadków znalezione przez nas młode zwierzę nie jest wcale porzucone . Matka z reguły obserwuje młode, a zbliża się do nich tylko na czas karmienia.
Są to naturalne zachowania i strategie ochronne zwierząt (młode zwierzę nie wydziela intensywnego zapachu, jest więc trudniej wyczuwalne przez drapieżniki, nie jest zbyt ruchliwe i ma maskujące ubarwienie).
Zabierając do domu czy nawet dotykając takie młode zwierzę robimy mu wielką krzywdę. Musimy mieć tego świadomość. Możemy przez to narazić je na niebezpieczeństwo ze strony drapieżników, porzucenie przez matkę lub uniemożliwić mu powrót do naturalnego środowiska.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański